The ISRO Computer Science (CS) Scientist Engineer test held on May 24, 2014 (Saturday). Total questions were 80 and test duration were 90 Minutes. Here is the solution of paper according to me of set A.
- The Final Answer Key 2014 for All Sets by ISRO: Click here
- For complete preparation for ISRO Computer Science visit my this article: Click Here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2016: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2015: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2013: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2011: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2009: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2008: Click here
- For ISRO Answer Key and Solutions Computer Science Scientist Engineer 2007: Click here
1. Consider a 33 MHz CPU based system. What is the number of wait states required if it is interfaced with a 60ns memory? Assume a maximum of 10ns delay for additional circuitry like buffering and decoding.
(a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wait_state- A wait state is a delay experienced by a computer processor when accessing external memory or another device that is slow to respond.
- CPU frequency is 33 MHz means 1 clock time is 1 / (33X106) = .03030 X 10-6 sec = 30.30 ns
- Memory access time is 60 ns + 10ns = 70 ns
- No. of wait states = No. of clocks to need = 70 ns / 30.30 ns = 2.31
- Implies that in 3rd clock operation will complete. So no. of wait states 2.
2. The number of states required by a Finite State Machine, to simulate the behavior of a computer with a memory capable of storing ‘m’ words, with each word being ‘n’ bits long is
(a) m x 2n (b) 2m+n (c) 2mn (d) m+n
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: We need to find the number of different configurations possible.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/3411/states-required-simulate-behavior-computer-capable-storing- A word is of n bits. And we have m such words. So, total number of bits = m*n
- We need a separate state for each bit combination. So, no. of states = 2mn
3. What is the output of the following C program?
#include <stdio.h>
#define SQR(x) (x*x)
int main()
{
int a;
int b=4;
a = SQR(b+2);
printf("%d\n",a);
return 0;
}
(a) 14 (b) 36 (c) 18 (d) 20
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: Traverse the value of SQR(b+2)
= (b+2*b+2)
= (4+2*4+2) = 14
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/49877/what-is-o-p-and-explain-pls
Correct Answer: (c)
= (b+2*b+2)
= (4+2*4+2) = 14
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/49877/what-is-o-p-and-explain-pls
4. Consider the following pseudo-code
while ( m< n)
if ( x > y) and (a < b) then
a=a+l
y=y-1
end if
m=m+l
end while
What is the cyclomatic complexity of the above pseudo-code?
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: Cyclomatic complexity is a quantitative measure of the number of linearly independent paths through a program's source code. Analyse the given code follows using control flow graph.
Correct Answer: (a)
A while ( m< n)
B,C if ( x > y) and (a < b) then
D a=a+l
E y=y-1
end if
F m=m+l
G end while
3 different ways to compute Cyclomatic Complexity (M):
M = E-V+2*K = 9-7+2*1 = 4
M = C + 1 = 3 + 1 = 4
M = Regions(CFG) = 4
where:
E=number of edges
V=number of vertices
K=number of graph components
C=number of conditions/decision points
Reference: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/32242464/calculation-of-cyclomatic-complexity-for-pseudocode
5. What is the number of steps required to derive the string ((() ()) ()) for the following grammar.
S → SS
S → (S)
S → ε
(a) 10 (b) 15 (c) 12 (d) 16
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: 10 derivation steps need to derive the given string starting from symbol S:
1. (S)
2. (SS)
3. ((S)S)
4. ((SS)S)
5. (((S)S)S)
6. ((()S)S)
7. ((()(S))S)
8. ((()())S)
9. ((()())(S))
10. ((()())())
Correct Answer: (b)
1. (S)
2. (SS)
3. ((S)S)
4. ((SS)S)
5. (((S)S)S)
6. ((()S)S)
7. ((()(S))S)
8. ((()())S)
9. ((()())(S))
10. ((()())())
6. The process of modifying IP address information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device is called
(a) Port address translation (PAT)
(b) Network address translation (NAT)
(c) Address mapping
(d) Port mapping
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: Network Address Translation (NAT) is the process where a network device, usually a firewall, assigns a public address to a computer (or group of computers) inside a private network.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_address_translation
Correct Answer: (d)
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_address_translation
7. What does a pixel mask mean?
(a) string containing only l’s
(b) string containing only 0’s
(c) string containing two 0’s
(d) string containing 1′s and 0’s
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation: Pixel mask is formed by digits 1 and 0 to determine the positions to create a plot within the line path. For example, the mask 1111000 is used to show a dashed line with a dash length of 4 and inter point spacing of 3.
Reference: http://www.andswaru.com/What-is-pixel-mask
Correct Answer: (c)
Reference: http://www.andswaru.com/What-is-pixel-mask
8. In the standard IEEE 754 single precision floating point representation, there is 1 bit for sign, 23 bits for fraction and 8 bits for exponent. What is the precision in terms of the number of decimal digits?
(a) 5 (b) 6 (c) 7 (d) 8
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: Precision is the number of digits we can represent accurately. IEEE 754 floating point representation have 23 precision bits and one implied bit (bit before point) makes it 24 precision bits. With 24 binary digits we can represent ___ decimal digits?
Correct Answer: (b)
 Explanation: Radian measure θ of a central angle of a circle is defined as the ratio of the length of the arc the angle subtends (s) and the radius of the circle (r).
Explanation: Radian measure θ of a central angle of a circle is defined as the ratio of the length of the arc the angle subtends (s) and the radius of the circle (r).
So, R/R = 1 Radian.
Reference: http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/algtrig/atm1/arclengthlesson.htm
Correct Answer: (d)
There is concept to determine: baseXno. of digits = baseYno. of digits
By following the concept: 224 = 10n
=> 24 log 2 = n log 10 => n = 24 log 2 => n = 24 * .30 => n = 7.22
Means 7 is the precision in terms of the number of decimal digits.
Reference: http://steve.hollasch.net/cgindex/coding/ieeefloat.html
9. Let R be the radius of a circle. What is the angle subtended by an arc of length R at the centre of the circle?
(a) 1 degree
(b) 1 radian
(c) 90 degrees
(d) π radians
Correct Answer: (b)
 Explanation: Radian measure θ of a central angle of a circle is defined as the ratio of the length of the arc the angle subtends (s) and the radius of the circle (r).
Explanation: Radian measure θ of a central angle of a circle is defined as the ratio of the length of the arc the angle subtends (s) and the radius of the circle (r).So, R/R = 1 Radian.
Reference: http://www.regentsprep.org/regents/math/algtrig/atm1/arclengthlesson.htm
10. The number of logical CPUs in a computer having two physical quad-core chips with hyper threading enabled is ____.
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 8 (d) 16
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation:
- There are two quad core chips, so total no. of physical CPU = 2 * 4 = 8.
- In hyper threading, every physical CPU corresponds to 2 logical CPU.
- Here 8 physical CPU corresponds to 8 * 2 = 16 logical CPU.
11. An aggregation association is drawn using which symbol?
(a) A line which loops back on to the same table
(b) A small open diamond at the end of a line connecting two tables
(c) A small closed diamond at the end of a line connecting two tables
(d) A small closed triangle at the end of a line connecting two tables
Correct Answer: (b)
 Explanation: An aggregation is a collection, or the gathering of things together. This question is about drawing of aggregation association in UML. The aggregation link usually used to stress the point that Class A is not the exclusive container of Class B, as in fact Class B has another container.The open diamond is used to show aggregation. Example: library has students and books. Here the student can exist without library, the relation between student and library is aggregation.
Explanation: An aggregation is a collection, or the gathering of things together. This question is about drawing of aggregation association in UML. The aggregation link usually used to stress the point that Class A is not the exclusive container of Class B, as in fact Class B has another container.The open diamond is used to show aggregation. Example: library has students and books. Here the student can exist without library, the relation between student and library is aggregation.12. How many states are there in a minimum state deterministic finite automaton accepting the language L = { w | w ∈ (0,1)*, number of 0’s is divisible by 2 and number of l’s is divisible by 5, respectively} ?
(a) 7 (b) 9 (c) 10 (d) 11
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Whenever "case 1 and case 2" is given for DFA, just multiply no. of states need for case 1 and number of states need for case 2 to find total states in DFA. So here states = 2 * 5 = 10.
13. Which of the following is TRUE with respect to a Reference?
(a) A reference can never be NULL
(b) A reference needs an explicit dereferencing mechanism
(c) A reference can be reassigned after it is established
(d) A reference and pointer are synonymous
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation:
- A reference can't be NULL, reference refers to some object, although it may or may not be valid.
- Reference doesn't need an explicit dereferencing mechanism.
- Once a reference is created, it cannot be later made to reference another object.
- Pointer stores the address whereas Reference is an alias of some variable.
14.
There are 200 tracks on a disk platter and the pending requests have
come in the order – 36, 69, 167, 76, 42, 51, 126, 12, and 199. Assume
the arm is located at the 1001h track and moving towards track 200. If
sequence of disc access is 126, 167, 199, 12, 36, 42, 51, 69, and 76
then which disc access scheduling policy is used?
(a) Elevator
(b) Shortest Seek-time First
(c) C-SCAN
(d) First Come First Served
(a) Elevator
(b) Shortest Seek-time First
(c) C-SCAN
(d) First Come First Served
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: These are algorithms designed for disk scheduling tasks.
- First Come-First Serve (FCFS): doesn't provide the best results, moves to fulfill FCFS.
- Shortest Seek Time First (SSTF): request is serviced according to next shortest distance.
- Elevator (SCAN): behaves as a building elevator, where the elevator continues to travel in its current direction until end of directions.
- Circular SCAN (C-SCAN): Circular Elevator Algorithm, time of the return seek is wasted because in return direction never services requests.
- LOOK: Similar to SCAN with one change, changes direction on last request.
- C-LOOK: Similar to C-SCAN with one change, changes direction on last request and first request.
15. Consider the logic circuit given below:
Q = _______________?
(a) A'C+BC'+CD
(b) ABC+C'D
(c) AB+BC'+BD'
(d) AB'+AC'+C'D
Q = _______________?
(a) A'C+BC'+CD
(b) ABC+C'D
(c) AB+BC'+BD'
(d) AB'+AC'+C'D
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: NAND gate produces complement of multiplication of inputted variables. Lets traverse the given circuit:
= (((CD)' . B)' . (AB)')'
= ((CD)' . B) + (AB)
= ((C' + D') . B) + (AB)
= (BC' + BD') + (AB)
= AB + BC' + BD'
16. What is routing algorithm used by OSPF routing protocol?
(a) Distance vector
(b) Flooding
(c) Path vector
(d) Link state
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol for Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It uses a link state routing algorithm and falls into the group of interior routing protocols, operating within a single autonomous system (AS).
- OSPF is the most widely used interior gateway protocol (IGP) in large enterprise networks.
- The basic concept of link-state routing is that every node constructs a map of the connectivity to the network, in the form of a graph, showing which nodes are connected to which other nodes. Each node then independently calculates the next best logical path from it to every possible destination in the network. The collection of best paths will then form the node's routing table.
- A distance-vector routing protocol requires that a router inform its neighbors of topology changes periodically. Examples of distance vector routing are RIPv1 and RIPv2, IGRP and Babel.
17. If each address space represents one byte of storage space, how many address lines are needed to access RAM chips arranged in a 4 x 6 array, where each chip is 8K x 4 bits?
(a) 13 (b) 15 (c) 16 (d) 17
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Number of chips = 4 * 6 = 24 => To address chips need 5 bits
Chip is byte addressable and number of bytes in a chip = (8K x 4) / 8 = 210+2 = 212
=> To address bytes of chips needs 12 bits
=> So total 17 address lines need in corresponding to 17 bits.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/15027/how-many-address-lines-are-needed-to-access-ram-chips
18. Consider the following segment table in segmentation scheme:
What happens if the logical address requested is – Segment Id 2 and Offset 1000?
(a) Fetches the entry at the physical address 2527 for Segment Id 2
(b) A trap is generated
(c) Deadlock
(d) Fetches the entry at offset 27 in Segment Id 3
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: Offset 1000 in Segment Id 2 is crossing the Segment Id 2 memory area. Here Segment Id 2 memory area is 1527 to 1527+498 = 2025.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/16942/what-happens-logical-address-requested-segment-offset-1000
19. The number of bit strings of length 8 that will either start with 1 or end with 00 is ______?
(a) 32 (b) 128 (c) 160 (d) 192
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation:
- String starting with 1 (S):
8 places where 1 place fixed and remaining 7 places can represent 2^7 = 128 values - String ending with 00 (E):
8 places where 2 place fixed and remaining 6 places can represent 2^6 = 64 values - Common strings (S∩E) will be there that have been counted twice.
8 places where 3 place fixed and remaining 5 places can represent 2^5 = 32 values
Ref: http://gateoverflow.in/15898/the-number-strings-length-that-will-either-start-with-end-with
20. Which of the following is not a maturity level as per Capability Maturity Model?
(a) Initial (b) Measurable (c) Repeatable (d) Optimized
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: The CMM model's aim is to improve existing software-development processes, but it can also be applied to other processes. There are five levels defined:
- Initial (chaotic, ad hoc, individual heroics) - the starting point for use of a new or undocumented repeat process.
- Repeatable - the process is at least documented sufficiently such that repeating the same steps may be attempted.
- Defined - the process is defined/confirmed as a standard business processes.
- Managed - the process is quantitatively managed in accordance with agreed-upon metrics.
- Optimizing - process management includes deliberate process optimization.
21. Consider the following sequential circuit.
What are values of Q0 and Q1 after 4 clock cycles, if the initial values are 00?
(a) 11 (b) 01 (c) 10 (d) 00
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Initial : 00 States Q0 and Q1 are zero
Clock 1: 11 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0.
Clock 2: 01 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
Clock 3: 10 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1.
Clock 4: 00 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
- T flip flop toggles the state if input T is 1, and does not change state if input T is 0.
- T flip flop is a clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered) flip flop.
- Edge triggered flip flops can only change its values at the edge of a clock, in absence of edge does not change its state, remains same.
- In given circuit, clock symbol is showing that it is positive edge triggering (low to high change). Note that there are mainly four different types of clock-triggering methods.
Initial : 00 States Q0 and Q1 are zero
Clock 1: 11 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0.
Clock 2: 01 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
Clock 3: 10 State Q0 changed to 1 because input T is 1 and previous state was 0 and State Q1 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1.
Clock 4: 00 State Q0 changed to 0 because input T is 1 and previous state was 1 and State Q1 remains same because clk value is 0.
22. Consider the schema R (A, B, C, D) and the functional dependencies A -> B and C -> D. If the decomposition is made as R1 (A, B) and R2(C, D), then which of the following is TRUE?(a) Preserves dependency but cannot perform lossless join
(b) Preserves dependency and performs lossless join
(c) Does not preserve dependency and cannot perform lossless join
(d) Does not preserve dependency but performs lossless join
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: While decomposing a relational table we must verify the following properties:
- Dependency Preserving Property: whether we can derive all the original FDs from the FDs present after decomposition? If yes then it is preserving.
- Lossless-Join Property: whether one of the following functional dependencies exist:
R1 ∩ R2 → R1 or R1 ∩ R2 → R2? If yes then it performs lossless join.
Reference: http://quiz.geeksforgeeks.org/gate-gate-cs-2001-question-23/
23. The test suite (set of test input) used to perform unit testing on a module could cover 70% of the code. What is the reliability of the module if the probability of success is 0.95 during above testing?
(a) 0.665 to 0.95
(a) 0.665 to 0.95
(b) At the most 0.665
(c) At the most 0.95
(c) At the most 0.95
(d) At least 0.665
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: I haven't got exact solution of this question.
Code covered for testing: 70%
Probability of success: 95%
Reliability = .70 * .95 = 0.665
I do not know how we can say that this reliability is at most or at least.
24. In a system an RSA algorithm with p = 5 and q = 11, is implemented for data security. What is the value of the decryption key if the value of the encryption key is 27?
(a) 3 (b) 7 (c) 27 (d) 40
(a) 3 (b) 7 (c) 27 (d) 40
Explanation: RSA algorithm is is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm. RSA involves a public key (encryption key) and private key (decryption key).
- Choose two different large random prime numbers p and q. Here already given p = 5, q =11.
- Calculate n = p*q where n is the modulus for the public key and the private keys. Here n = 55.
- Calculate the totient: ϕ = (p − 1) * (q − 1). Here ϕ = 40.
- Choose an encryption key integer e such that 1 < e < ϕ and e is co-prime to ϕ
i.e. e and ϕ share no factors other than 1 or we can say gcd(e, ϕ) = 1.
Here e is already given that is e = 27. - Compute an decryption key d to satisfy the congruence relation d * e ≡ 1 mod ϕ.
Here we require to find out the value of decryption key.
d * 27 = 1 mod 40 => d = 81
25. Suppose you want to build a memory with 4 byte words and a capacity of 221 bits. What is type of decoder required if the memory is built using 2K x 8 RAM chips?
(a) 5 to 32 (b) 6 to 64 (c) 4 to 16 (d) 7 to 128
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: Decoder is an electronic circuit with multiple inputs and multiple outputs. Here to built memory, decoder will help to select required memory chips as per the need.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/4755/how-many-2k-x-8-ram-chips-are-needed- 2K x 8 denotes there is 2K = 211 cells and 11 address lines needs to select a cell.
- Total need of RAM chips is = 221 / (2K x 8) = 27 = 128
- RAM chips will be used in groups of 4 because word size is 4 byte. At any time 4 RAM chips will be selected together and a byte can be fetched in parallel from all these, resulting in 4 bytes being fetched in 1 memory cycle. Here RAM chip groups = 128/4 = 32.
- To select any RAM chip group out of 32 needs 5 lines to 32 lines decoder.
26. The output of a tristate buffer when the enable input in 0 is
(a) Always 0
(b) Always 1
(c) Retains the last value when enable input was high
(d) Disconnected state
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation:
27. How many different BCD numbers can be stored in 12 switches? (Assume two position or on-off switches).
(a) 212 (b) 212-1 (c) 1012 (d) 103
Correct Answer: (d)
28. Suppose there are eleven items in sorted order in an array. How many searches are required on the average, if binary search is employed and all searches are successful in finding the item?
(a) 3.00 (b) 3.46 (c) 2.81 (d) 3.33
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: The question is about of number of searches. Mid (root) element will require 1 search. 2nd level elements will require 2 searches and 3rd level elements will require 3 searches and so on. In this way, total number of searches for 11 elements = 1+(2+2)+(3+3+3+3)+(4+4+4+4) = 33. And average of this is 33/11 = 3.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/16124/many-searches-required-the-average-binary-search-employed
29. Consider the following Java code fragment. Which of the following statement is true?
Line No Code Statement
1 public class While
2 {
3 public void loop()
4 {
5 int x = 0;
6 while (1)
7 {
8 System.out.println("x plus one is " + (x+l));
9 }
10 }
11 }
(a) There is syntax error in line no. 1
(b) There are syntax errors in line nos. 1 & 6
(c) There is syntax error in line no. 8
(d) There is syntax error in line no. 6
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation: Java can use reserved keywords in class name (read here), so there is no error in line 1.
Here error is in line number 6: incompatible types: int cannot be converted to boolean.
In java, code while(1){ System.out.println("Hello"); } gives error while code while(true){ System.out.println("Hello"); } never give any error (check code).
27. How many different BCD numbers can be stored in 12 switches? (Assume two position or on-off switches).
(a) 212 (b) 212-1 (c) 1012 (d) 103
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation: With 4 bit we can represent BCD numbers 0 to 9. With 12 bits (12 switches) we can represent 0 to 9 numbers 3 times. Means 0 to 999; means 1000 numbers; means 10^3.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/13388/solve28. Suppose there are eleven items in sorted order in an array. How many searches are required on the average, if binary search is employed and all searches are successful in finding the item?
(a) 3.00 (b) 3.46 (c) 2.81 (d) 3.33
Correct Answer: (a)
Explanation: The question is about of number of searches. Mid (root) element will require 1 search. 2nd level elements will require 2 searches and 3rd level elements will require 3 searches and so on. In this way, total number of searches for 11 elements = 1+(2+2)+(3+3+3+3)+(4+4+4+4) = 33. And average of this is 33/11 = 3.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/16124/many-searches-required-the-average-binary-search-employed
29. Consider the following Java code fragment. Which of the following statement is true?
Line No Code Statement
1 public class While
2 {
3 public void loop()
4 {
5 int x = 0;
6 while (1)
7 {
8 System.out.println("x plus one is " + (x+l));
9 }
10 }
11 }
(a) There is syntax error in line no. 1
(b) There are syntax errors in line nos. 1 & 6
(c) There is syntax error in line no. 8
(d) There is syntax error in line no. 6
Correct Answer: (d)
Explanation: Java can use reserved keywords in class name (read here), so there is no error in line 1.
Here error is in line number 6: incompatible types: int cannot be converted to boolean.
In java, code while(1){ System.out.println("Hello"); } gives error while code while(true){ System.out.println("Hello"); } never give any error (check code).
30. Every time the attribute A appears, it is matched with the same value of attribute B but not the same value of attribute C. Which of the following is true?
(a) A -> (B, C)
(b) A -> B, A ->> C
(c) A -> B, C ->> A
(d) A ->> B, B -> C
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: Symbol ->> shows multi-value dependencies. If A ->> C is a dependency it means, for A, C has more than one value. Question is saying whenever A appears B has same value which is true in case of functional dependency A -> B, it means whenever A value repeats there be same B value. Also saying C is not same, it means for same A it contains multiple value of c.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/16128/which-of-the-following-is-true
42. Let x,y,z,a,b,c be the attributes of an entity set E. If {x}, {x,y}, {a,b}, {a,b,c} ,{x,y,z} are superkeys then which of the following are the candidate keys?
(a){x,y} and {a,b}
(b){x} and {a,b}
(c){x,y,z} and {a,b,c}
(d){z} and {c}
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation: In list of all the superkeys, minimal superkeys are candidate key. In given {x} and {a,b} are minimal superkeys so they are candidate keys.
Reference: http://gateoverflow.in/17425/which-of-the-following-are-the-candidate-keys
63. Consider the following Table

The table is in which normal form?
(a) First Normal Form
(b) Second Normal Form
(c) Third Normal Form but not BCNF
(d) Third Normal From and BCNF
Correct Answer: (c)
Explanation: To find normal form, follow this easy approach suggested by stinaq.me.
- First normal form: Are all the attributes atomic? Yes.
- Second normal form: Is there a non primary attribute that’s determined by parts of a candidate key? No.
- Third normal form: Does a non primary attribute exists that is determined by another non primary attribute? No.
- Boyce-Codd normal form: Are all attributes to the left of the arrows candidate keys? No. Here given table is also having a C -> D dependency where C is not a candidate key. So given table is not in BCNF.





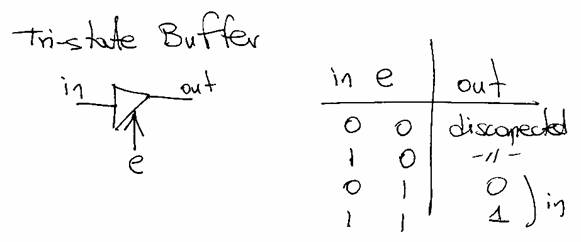
Keep doing,its very useful
ReplyDelete